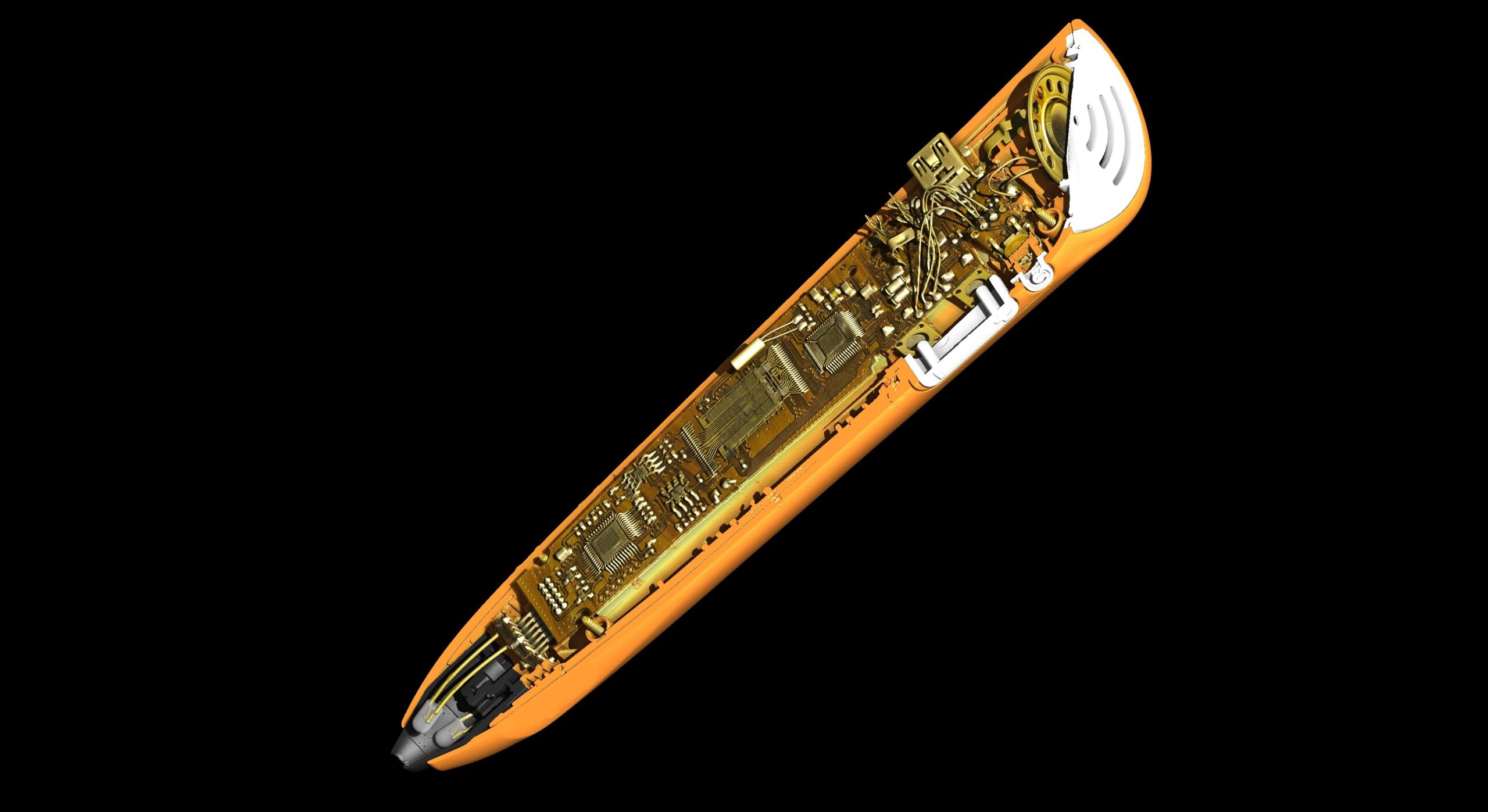
With medical devices, failure is not an option
From the simple to the most complex applications, the reproducible examination and inspection of key medical components is vital. The Nikon X-ray and CT range, known as VOXLS, ensures no area is inaccessible. With the high image resolution and ultra-fast CT reconstruction, the sharp images provide a fundamental insight to ensure reliable and repeatable performances.
With May’s Scan of the Month, we would like to show you that X-ray CT is particularly suited to verify the dimensions of stents, dental implants, pacemakers and many more medical devices.
This month, 3D MEDLAB, a pioneer in additive manufacturing in the medical device sector, has used a MCT 225 to scan various 3D-printed implants made from metal or polymer. The aim was to perform both material porosity and surface roughness analysis.
In the dental segment, CT is performed to verify correct positioning and orientation of dentures on prosthesis crafted by dental technicians. It provides geometric information that allows them to fine tune each individual denture design before it is manufactured and installed into the patient’s mouth.
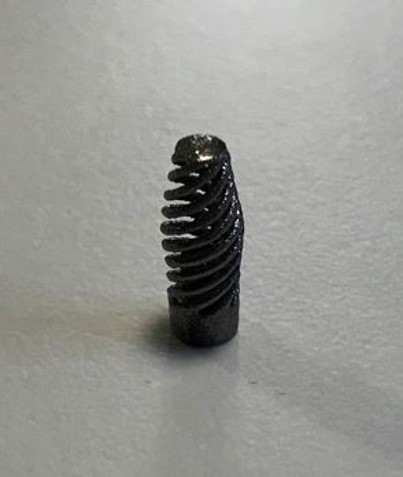
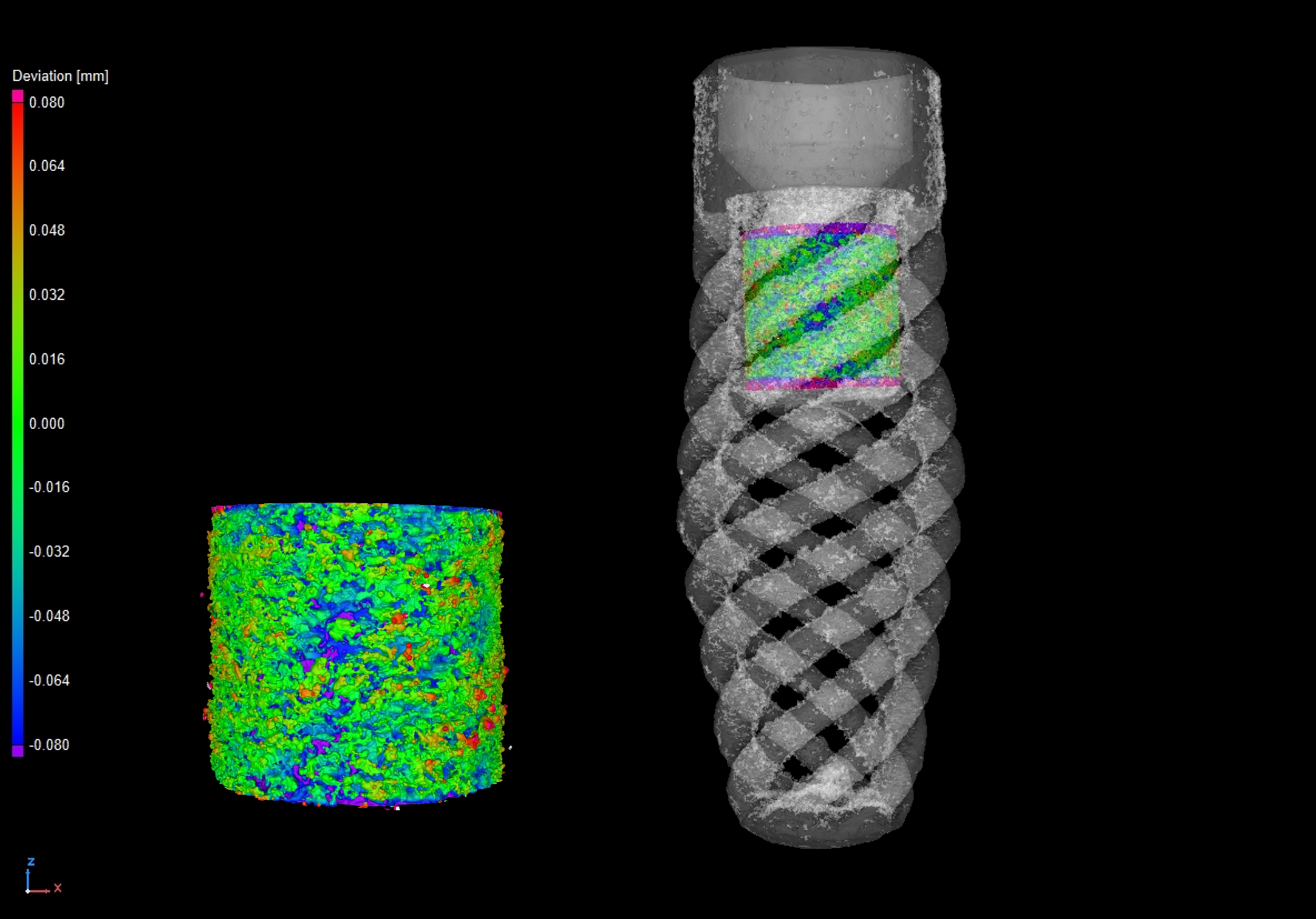
Photo of a dental implant made of titanium niobium (TiNb) provided by 3DMedlab and AST Innovations. The scans have been done with a resolution of 7,1 µm, showing the high level of internal detail visible from the reconstruction data.
The dental implant X-ray CT scan was completed using a circular scan at an X-ray power of 7 Watts and a voxel resolution of 7.1 µm, using a Nikon MCT 225. This system comes equipped with a 225 kV, 225 W reflection target. This scan was performed using the 225 kV reflection target option coupled with a Varex XRD 1620CT flat panel detector. The detector captured 3141 projections (individual radiographs) at an exposure time of 2000 ms, resulting in a total scan time of 2 hours. This is longer than the normal CT scan of 1-5 minutes, because of the extremely high resolution and complex material. The X-ray CT data was reconstructed using Nikon CT Pro 3D and rendered in Volume Graphics Studio Max 2022.3. A porosity analysis was performed on the whole implant and a partial roughness analysis was performed.
Material researchers are also developing implants made of titanium foam that offer favorable biocompatibility and superior surface roughness and strength.
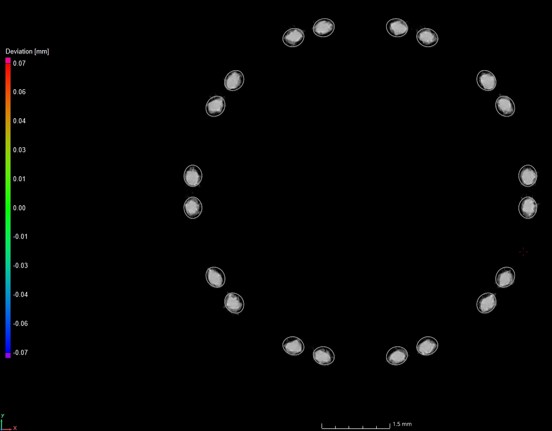
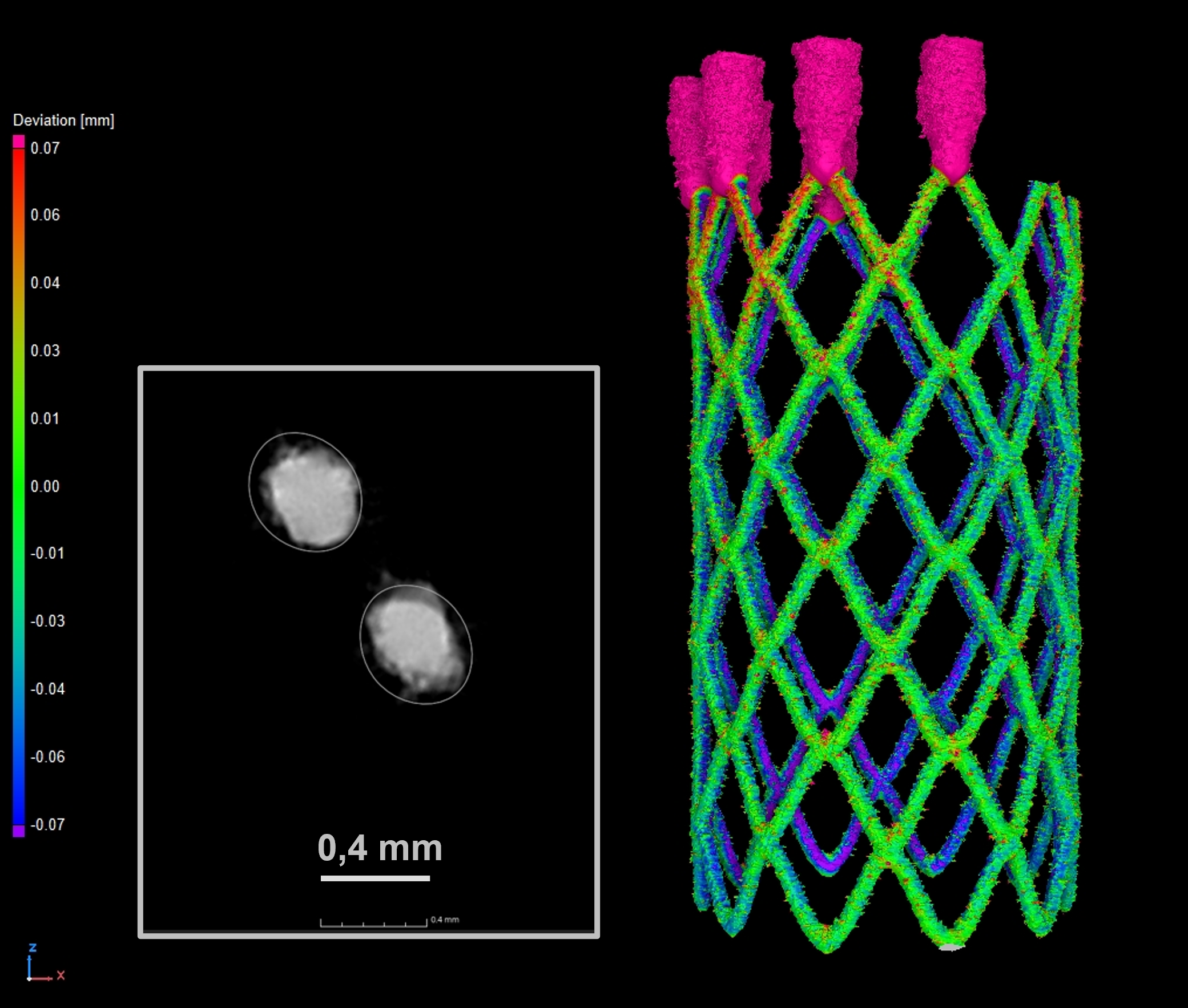
Scans of a heart stent made of Nitinol (shape memory alloy) with a resolution of 11 µm
The heart stent X-ray CT scan was achieved using the same machine at an X-ray power of 11 W and a voxel resolution of 11.4 µm. The detector captured 3141 projections at an exposure time of 1415 ms, resulting in a total scan time of 1 hour and 15 min. A nominal/actual comparison was performed on the volume and its corresponding CAD file, showing the difference between the geometry of the CAD file and the 3D printed implant.
By literally looking inside key components and critical assemblies, X-ray and CT face no limitations for accessing hard-to-reach spots. That’s why the Nikon X-ray CT system is a key tool in the examination of medical devices and components. It provides the means to examine failures; assessing whether they are due to a manufacturing error or misuse.